An Introduction to Heat

Overview
Heat 从 Havana 起成为 OpenStack 的正式项目,它的定位相当于 AWS 的 CloudFormation,为多种云平台的云服务乃至虚拟机的应用程序提供编排的功能。所谓的编排,就是按照特定的顺序执行某些操作。我们以用户需要创建一个 instance 和 volume,然后挂载 volume 至 instance 为例,一般的步骤为:
调用 Nova 创建 instance
|
v
调用 Cinder 创建 volume
|
v
调用 nova 挂载 volume 至 instance
如果利用 heat,用户只需在一个文本的 template 中定义上述的资源和操作步骤,然后调用 heat stack-create 即可,heat 会自动的解析 template 里内容和依赖关系,最后按照顺序调用相关组件的 API 依次创建 instance、volume 并挂载 volume。如此,用户可以非常便捷的构建 IT 设施和部署应用,极大的简化了中间繁杂的步骤。
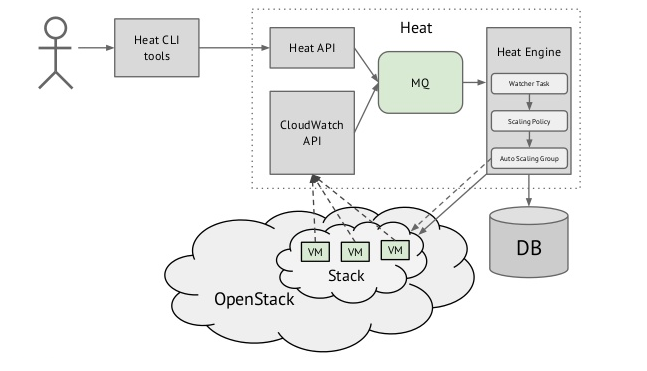
Heat 的架构如下,它由 4 部分组成:
- heat-api: 提供原生的 Restful API
- heat-api-cfn: 兼容 AWS CloudFormation API
- heat-api-cloudwatch: 兼容 AWS CloudWatch API,可用于接收 ceilometer 的告警
- heat-engine: 最核心部分,解析 template,处理逻辑业务,完成资源的创建和部署
Orchestration
Orchestration 是 heat 最重要的功能,和 RESTful API 把一切都抽象为 resource 相同,heat 也把所有的云服务,如 instance、flavor、volume、network、ip 乃至 volumeattachment、softwaredeployment 都抽象为 resource,每种的 resource 都有自身的 properties,比如 flavor 类型的 resource,它有 ram、vcpu 和 disk 等 properties。Template 用文本定义一系列的 resource,heat 解析 template 的 resource,然后生成一个 stack,stack 表示这些 resource 的集合,最后根据依赖关系,依次完成各种资源的创建。
- template: 文本模块,定义各种 resource,支持 AWS 和 HOT 格式的模板
- stack: stack 是一组 resource 的集合,heat 根据 template 创建 stack
- resource: 云服务,如 instance, flavor 等
- properties: 表示 resource 的某些属性
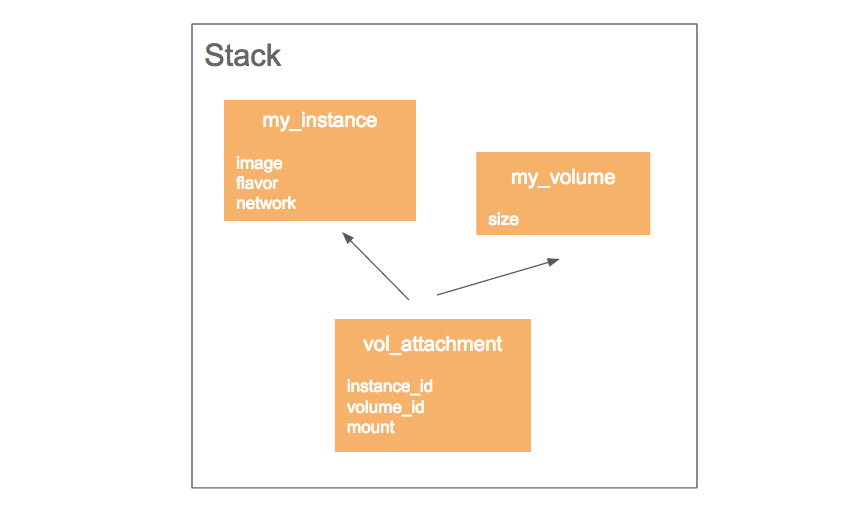
例如,下述 template 创建一个 instance 和 volume,并把 volume 挂载到 instance:
heat_template_version: 2013-05-23
description: >
A HOT template that holds a VM instance with an attached
Cinder volume. The VM does nothing, it is only created.
resources:
my_instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: your_image_id
flavor: m1.small
networks: [{network: your_network_id }]
my_volume:
type: OS::Cinder::Volume
properties:
size: 10
vol_attachment:
type: OS::Cinder::VolumeAttachment
properties:
instance_uuid: { get_resource: my_instance }
volume_id: { get_resource: my_vol }
mountpoint: /dev/vdb
Heat 支持多种类型的 resource,用户也可以加入自己定义的 resource:
AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup
......
AWS::S3::Bucket
OS::Ceilometer::Alarm
OS::Ceilometer::CombinationAlarm
OS::Cinder::EncryptedVolumeType
OS::Cinder::Volume
OS::Cinder::VolumeAttachment
OS::Glance::Image
OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup
......
OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle
OS::Keystone::Endpoint
......
OS::Neutron::LBaaS::PoolMember
OS::Neutron::LoadBalancer
......
OS::Nova::Server
......
Autoscaling
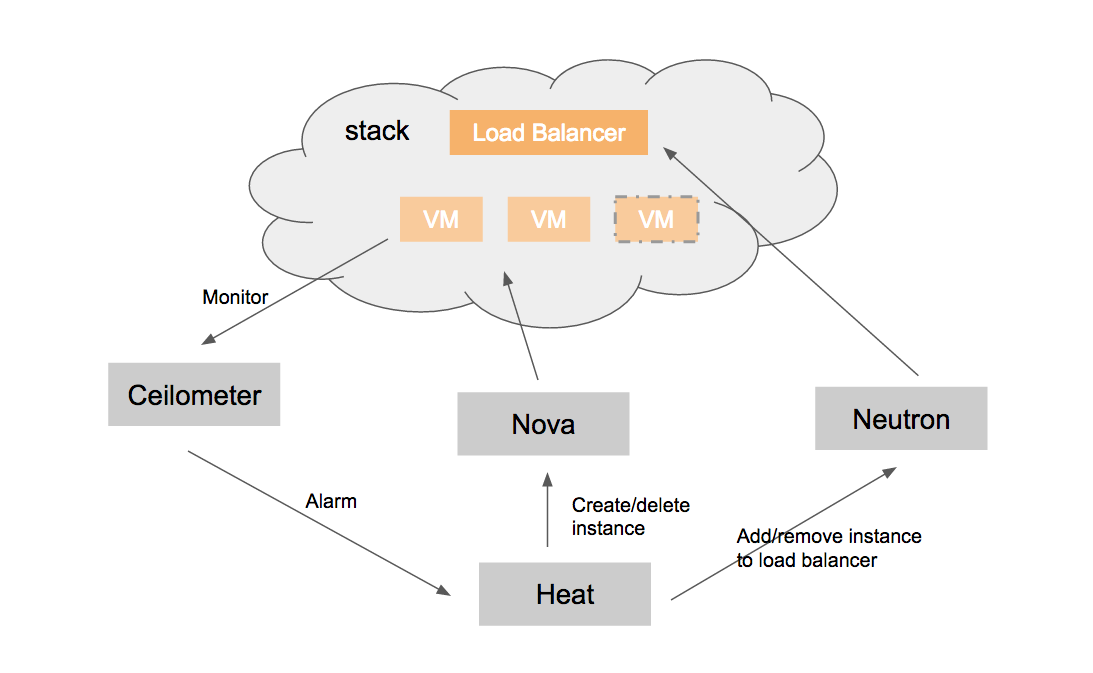
Autoscaling 是 Heat 的另外一大特性,它通过 ceilometer 监控伸缩组(scaling group)的虚拟机的负载,当虚拟机的负载超过阈值时,ceilometer 发送告警给 heat,heat 收到告警后,根据伸缩策略(scaling policy)增加虚拟机,并将虚拟机加入到 load balancer 的 backends 中;反之,当虚拟机的负载很低时,heat 收到告警后删除虚拟机。
官方推荐的 autoscaling template 如下:
heat_template_version: 2013-05-23
description: AutoScaling Wordpress
parameters:
image:
type: string
description: Image used for servers
key:
type: string
description: SSH key to connect to the servers
flavor:
type: string
description: flavor used by the web servers
database_flavor:
type: string
description: flavor used by the db server
network:
type: string
description: Network used by the server
subnet_id:
type: string
description: subnet on which the load balancer will be located
database_name:
type: string
description: Name of the wordpress DB
default: wordpress
database_user:
type: string
description: Name of the wordpress user
default: wordpress
external_network_id:
type: string
description: UUID of a Neutron external network
resources:
db:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
flavor: {get_param: database_flavor}
image: {get_param: image}
key_name: {get_param: key}
networks: [{network: {get_param: network} }]
user_data_format: RAW
user_data:
str_replace:
template: |
#!/bin/bash -v
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
systemctl enable mariadb.service
systemctl start mariadb.service
mysqladmin -u root password $db_rootpassword
cat << EOF | mysql -u root --password=$db_rootpassword
CREATE DATABASE $db_name;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON $db_name.* TO "$db_user"@"%"
IDENTIFIED BY "$db_password";
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT
EOF
params:
$db_rootpassword: {get_attr: [database_root_password, value]}
$db_name: {get_param: database_name}
$db_user: {get_param: database_user}
$db_password: {get_attr: [database_password, value]}
asg:
type: OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup
properties:
min_size: 1
max_size: 3
resource:
type: lb_server.yaml
properties:
flavor: {get_param: flavor}
image: {get_param: image}
key_name: {get_param: key}
network: {get_param: network}
pool_id: {get_resource: pool}
metadata: {"metering.stack": {get_param: "OS::stack_id"}}
user_data:
str_replace:
template: |
#!/bin/bash -v
yum -y install httpd wordpress
systemctl enable httpd.service
systemctl start httpd.service
setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db=1
sed -i "/Deny from All/d" /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf
sed -i "s/Require local/Require all granted/" /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf
sed -i s/database_name_here/$db_name/ /etc/wordpress/wp-config.php
sed -i s/username_here/$db_user/ /etc/wordpress/wp-config.php
sed -i s/password_here/$db_password/ /etc/wordpress/wp-config.php
sed -i s/localhost/$db_host/ /etc/wordpress/wp-config.php
systemctl restart httpd.service
params:
$db_name: {get_param: database_name}
$db_user: {get_param: database_user}
$db_password: {get_attr: [database_password, value]}
$db_host: {get_attr: [db, first_address]}
web_server_scaleup_policy:
type: OS::Heat::ScalingPolicy
properties:
adjustment_type: change_in_capacity
auto_scaling_group_id: {get_resource: asg}
cooldown: 60
scaling_adjustment: 1
web_server_scaledown_policy:
type: OS::Heat::ScalingPolicy
properties:
adjustment_type: change_in_capacity
auto_scaling_group_id: {get_resource: asg}
cooldown: 60
scaling_adjustment: -1
cpu_alarm_high:
type: OS::Ceilometer::Alarm
properties:
description: Scale-up if the average CPU > 50% for 1 minute
meter_name: cpu_util
statistic: avg
period: 60
evaluation_periods: 1
threshold: 50
alarm_actions:
- {get_attr: [web_server_scaleup_policy, alarm_url]}
matching_metadata: {'metadata.user_metadata.stack': {get_param: "OS::stack_id"}}
comparison_operator: gt
cpu_alarm_low:
type: OS::Ceilometer::Alarm
properties:
description: Scale-down if the average CPU < 15% for 10 minutes
meter_name: cpu_util
statistic: avg
period: 600
evaluation_periods: 1
threshold: 15
alarm_actions:
- {get_attr: [web_server_scaledown_policy, alarm_url]}
matching_metadata: {'metadata.user_metadata.stack': {get_param: "OS::stack_id"}}
comparison_operator: lt
monitor:
type: OS::Neutron::HealthMonitor
properties:
type: TCP
delay: 5
max_retries: 5
timeout: 5
pool:
type: OS::Neutron::Pool
properties:
protocol: HTTP
monitors: [{get_resource: monitor}]
subnet_id: {get_param: subnet_id}
lb_method: ROUND_ROBIN
vip:
protocol_port: 80
lb:
type: OS::Neutron::LoadBalancer
properties:
protocol_port: 80
pool_id: {get_resource: pool}
# assign a floating ip address to the load balancer
# pool.
lb_floating:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIP
properties:
floating_network_id: {get_param: external_network_id}
port_id: {get_attr: [pool, vip, port_id]}
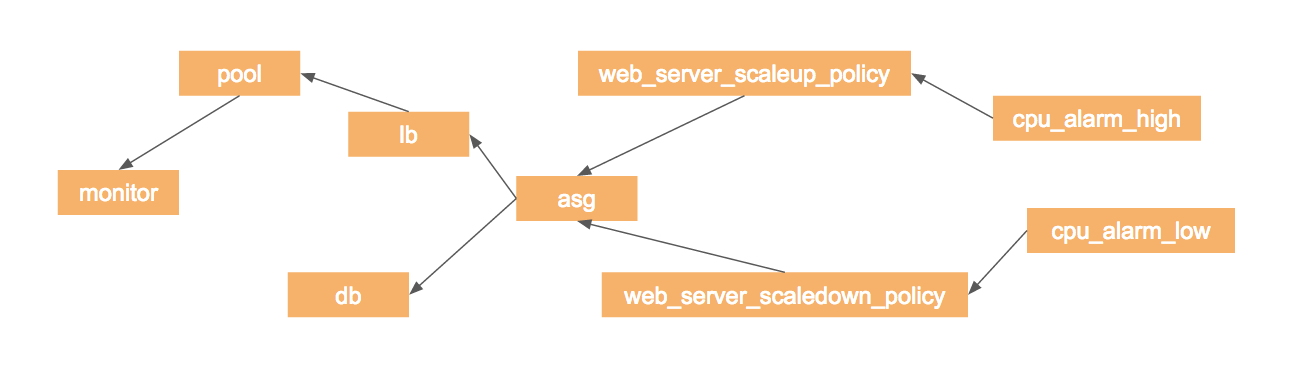
这些 resource 的依赖关系如下:
Software Configuration and Deployment
虚拟机业务的初始化部署同样是 heat 重要的功能,它要求虚拟机镜像已安装 cloud-init,支持初始化虚拟机的以下信息等:
- hostname
- password
- ssh key
- 要安装的包
- bash 脚本
- ……
它把这些信息存放于 nova 的 userdata 和 metadata,当虚拟机启动后,由 cloud-init 消费这些信息,完成虚拟机业务的初始化部署和配置。Heat 专门提供了如下 resource 用于虚拟机业务的部署和配置:
- OS::Heat::MultipartMime
- OS::Heat::CloudConfig
- OS::Heat::SoftwareConfig
- OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployment
- OS::Heat::StructuredConfig
- OS::Heat::StructuredDeployment
OpenStack 西安 Meetup 黄填华演讲的 Heat-Software-Config 详细地介绍了 software configuration 和 deployment。